Common Linux commands for starters
Ten commonly used Linux commands for beginners
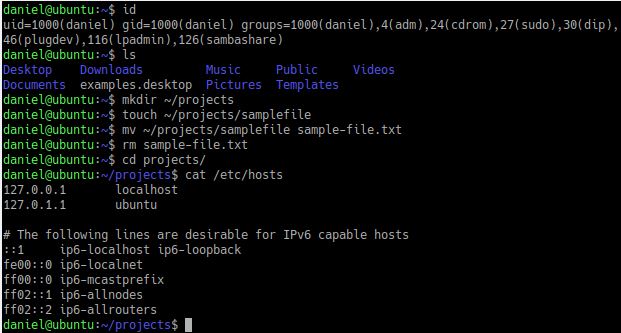
1. id – display information about user.
id will print the user and group information of the given argument, if no argument is given, it will show the information of the currently logged in user.
$ id uid=1000(daniel) gid=1000(daniel) groups=1000(daniel),4(adm),27(sudo) $ id -u -n daniel $ id root uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root) $ id sshd uid=110(sshd) gid=65534(nogroup) groups=65534(nogroup)
2. ls – list files in a directory.
ls lists the contents of current directory if not arguments are given. It has probably one of the largest number of options compared to other Linux commands.
$ pwd # our current working directory
/home/daniel/projects
$ ls # content of current directory
demo.txt mail nfs redhat samba
$ ls -l # long listing
total 20
-rw-rw-r-- 1 daniel daniel 21 Apr 15 01:04 demo.txt
drwxrwxr-x 2 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:04 mail
drwxrwxr-x 2 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:04 nfs
drwxrwxr-x 2 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:04 redhat
drwxrwxr-x 2 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:04 samba
$ ls -1 # list one file per line
demo.txt
mail
nfs
redhat
samba
$ ls -a # show all, including ones starting with . (dot)
. .. demo.txt .hidden mail nfs redhat samba
$ ls -al # long listen plus show all
total 32
drwxrwxr-x 6 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:04 .
drwxr-xr-x 18 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:06 ..
-rw-rw-r-- 1 daniel daniel 21 Apr 15 01:04 demo.txt
-rw-rw-r-- 1 daniel daniel 32 Apr 15 01:03 .hidden
drwxrwxr-x 2 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:04 mail
drwxrwxr-x 2 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:04 nfs
drwxrwxr-x 2 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:04 redhat
drwxrwxr-x 2 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:04 samba
# ls --format=verbose # same as ls -l
total 20
-rw-rw-r-- 1 daniel daniel 21 Apr 15 01:04 demo.txt
drwxrwxr-x 2 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:04 mail
drwxrwxr-x 2 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:04 nfs
drwxrwxr-x 2 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:04 redhat
drwxrwxr-x 2 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:04 samba
$ ls -F # classify: / for directory, * for executable, @ for symbolic link
demo-link@ demo.txt mail/ nfs/ redhat/ run.sh* samba/
$ ls -ls /etc/h* # sort by size, smallest first for all files starting with h in /etc/ directory
8 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4781 Mar 17 2016 /etc/hdparm.conf
4 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 92 Oct 22 2015 /etc/host.conf
4 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 12 Feb 18 01:21 /etc/hostname
4 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 191 Feb 18 01:21 /etc/hosts
4 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 411 Feb 18 01:29 /etc/hosts.allow
4 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 711 Feb 18 01:29 /etc/hosts.deny
3. cat – concatenate files and print on the standard output.
cat conCATenates one or more files given as argument and prints those on the standard output (console).
If no file or ‘-‘ (dash) is given, it reads from standard input until EOF (Ctrl+D) is pressed and prints is to standard output.
$ ls -l linus # ls to make sure file exists
-rw-rw-r-- 1 daniel daniel 403 Apr 15 01:20 linus
$ cat linus # print content of file to stdout
Hello everybody out there using minix -
I'm doing a (free) operating system (just a hobby, won't be big and professional like gnu) for 386(486) AT clones.
This has been brewing since april, and is starting to get ready.
I'd like any feedback on things people like/dislike in minix,
as my OS resembles it somewhat (same physical layout of the file-system (due to practical reasons) among other things).
$ cat -n linus # show line numbers with -n
1 Hello everybody out there using minix -
2
3 I'm doing a (free) operating system (just a hobby, won't be big and professional like gnu) for 386(486) AT clones.
4 This has been brewing since april, and is starting to get ready.
5 I'd like any feedback on things people like/dislike in minix,
6 as my OS resembles it somewhat (same physical layout of the file-system (due to practical reasons) among other things).
$ cat # read from stdin(keyboard) and print to stdout(screen), repeats after me until I press Ctr+D to end it.
reading
reading
from standard inpu
from standard inpu
pressing Ctr+D now
pressing Ctr+D now
$ cat << EOF > file-from-stdin # Reads from keyboard until EOF is pressed and saves(redirects) the text to a file.
I read this from stdin
end of file
EOF
$ ls -l file-from-stdin # printing content of file we created above.
-rw-rw-r-- 1 daniel daniel 35 Apr 15 01:22 file-from-stdin
$ cat file-from-stdin
I read this from stdin
end of file
4. clear – clears the terminal screen.
clear is self-explanatory, it clears the terminal display and places your cursor at the top left corner. Similar to “cls” command in DOS/Windows/PowerShell.
$ clear
5. rm – removes one or more files.
ls # list of files/dirs in current directory demo-link demo.txt file-from-stdin linus mail myfile nfs redhat run.sh samba $ ls myfile # file exists myfile $ rm myfile # delete file $ ls myfile # we should get an error ls: cannot access 'myfile': No such file or directory $ rm -i linus # prompt for confirmation before removing file rm: remove regular file 'linus'? y $ rm -v demo.txt # add verbosity, explain what is being done. removed 'demo.txt' $ rm -d mail -v # remove empty directory removed directory 'mail' $ rm redhat/ # try to delete directory with rm, should get an error rm: cannot remove 'redhat/': Is a directory $ rm -d redhat # error again, not empty rm: cannot remove 'redhat': Directory not empty $ rm -r redhat/ -v # use -r for recursive removal of directory and its contents. removed 'redhat/version7' removed 'redhat/version6' removed directory 'redhat/'
Use rmdir to delete the named directory, not its contents. To completely wipe out a directory and its contents use ‘rm -r’.
6. mkdir – make or create one or more directories.
mkdir is used to create one or more directories under current directory if no directory argument is given. The user creating the directory must have the permission to create a directory under the specified directory.
$ whoami # regular user daniel $ mkdir /root/mydir # trying to create directory under root user's home directory, should get permission error. mkdir: cannot create directory ‘/root/mydir’: Permission denied $ pwd # current working directory, my home directory /home/daniel/projects $ mkdir april-15 # create directory here $ ls april-15 demo-link file-from-stdin nfs run.sh $ mkdir nfs -v # can't overwrite an existing directory mkdir: cannot create directory ‘nfs’: File exists $ mkdir newdir/seconddir/thriddir # can't create a series of directories without parent directories existing mkdir: cannot create directory ‘newdir/seconddir/thriddir’: No such file or directory $ mkdir -p newdir/seconddir/thriddir # -p makes parent directories as well, solves above problem. $ ls -R newdir/ # recursive (-R) listing with ls shows all directories created. newdir/: seconddir newdir/seconddir: thriddir newdir/seconddir/thriddir:
7. mv – moves a file or directory to another location.
mv is most commonly used for renaming files and directories. You can specify more than two directory arguments,
it will move the all directory, except the last one to the last (destination) directory.
$ mv -v run.sh run-script.sh # -v is for verbose, move file. 'run.sh' -> 'run-script.sh' $ ls run* # file has been renamed. run-script.sh $ mv samba/ nfs/ redhat/ -v # move first two directories to the last one 'samba/' -> 'redhat/samba' 'nfs/' -> 'redhat/nfs' $ ls redhat/ nfs samba
8. cp – copy files and directories.
cp is used to copy files as well as directories, most commonly to take backups.
$ ls april-15 demo demo-link demo.txt file-from-stdin hosts-backup linus mail myfile newdir redhat run-script.sh $ cp demo demo-new -v # copying directory cp: omitting directory 'demo' $ cp -r demo demo-new -v # recursive(-r) copy, with verbose(-v) mode. 'demo' -> 'demo-new/demo' 'demo/one' -> 'demo-new/demo/one' $ cp -av redhat /tmp/ # archive, preserve the specified attributes 'redhat' -> '/tmp/redhat' 'redhat/nfs' -> '/tmp/redhat/nfs' 'redhat/samba' -> '/tmp/redhat/samba' 'redhat/newdir' -> '/tmp/redhat/newdir' 'redhat/newdir/seconddir' -> '/tmp/redhat/newdir/seconddir' 'redhat/newdir/seconddir/thriddir' -> '/tmp/redhat/newdir/seconddir/thriddir' $ls -al /tmp/redhat/ total 20 drwxrwxr-x 5 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:55 . drwxrwxrwt 13 root root 4096 Apr 15 01:58 .. drwxrwxr-x 3 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:55 newdir drwxrwxr-x 2 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:04 nfs drwxrwxr-x 2 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:51 samba $ touch demo/one mail/one $ cp demo/one mail/one # overwrite file $ cp -i demo/one mail/one # prompt before overwriting a file cp: overwrite 'mail/one'? y $ cp -s demo-link demo-link2 # copy as symbolic link $ ls -l ... lrwxrwxrwx 1 daniel daniel 8 Apr 15 01:51 demo-link -> demo.txt lrwxrwxrwx 1 daniel daniel 9 Apr 15 02:02 demo-link2 -> demo-link drwxrwxr-x 2 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:58 demo-new ... $ cp demo-link demo-link3 # copies target or dereferenced file, not symbolic link. $ ls -l ... drwxrwxr-x 2 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 02:00 demo lrwxrwxrwx 1 daniel daniel 8 Apr 15 01:51 demo-link -> demo.txt lrwxrwxrwx 1 daniel daniel 9 Apr 15 02:02 demo-link2 -> demo-link -rw-rw-r-- 1 daniel daniel 21 Apr 15 02:02 demo-link3 drwxrwxr-x 2 daniel daniel 4096 Apr 15 01:58 demo-new -rw-rw-r-- 1 daniel daniel 21 Apr 15 01:51 demo.txt ...
9. cd – change directory.
cd is actually a built-in shell command, you won’t find it in the file system as the other commands above. It is used to change working directory.
Use it with “pwd” to show your current directory.
$ pwd # our current working directory /home/daniel/projects $ cd demo # changing to demo/ directory $ pwd /home/daniel/projects/demo $ cd - # switch back to previous directory, "-" (dash) does the trick. /home/daniel/projects $ pwd /home/daniel/projects $ cd /root/ # you need permission to switch to protected directories. -bash: cd: /root/: Permission denied
10. man – display information from the man pages.
The man command provides and interface to the on-line reference manuals. man will search through all the sections of the man pages.
If the section number is given, it will search only that section.
$ man man # search the man pages for information about the man command. $ man ls # help on ls $ man 5 crontab # search in section 5 of the man pages $ man -k mkdir # show short description of mkdir keyword. mkdir (1) - make directories mkdir (2) - create a directory mkdirat (2) - create a directory